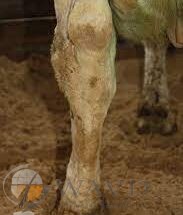
Papillomatosis is an infectious, highly contagious common viral and neoplastic disease of the skin, observed in cattle, manifested as multiple benign tumors that can progress to the malignant tumor . It is caused by papillomaviruses which are small, non-enveloped, icosahedral viruses, keeping double-stranded DNA viruses with circular genomes about 8000 base pairs long that replicate intranuclearly in infected cells. Papillomaviruses have a high predilection for stratified squamous epithelia of warm-blooded animals .
The disease is commonly stirring in young animals and also it may be occurring in all ages that affect cattle and other ungulates such as red deer, roe deer, elk, and less frequently in horses, dog, cat, sheep, goat, pig, and bison, including birds . BPV is strictly species-specific and does not infect any host other than natural one with exceptional vires BPV1, BPV2, and more rarely BPV13 that can jump species, although their natural host is bovine, they can infect equine and produce sarcoid at their injection site .
Bovine papillomatosis is located in different body parts including the skin, upper gastrointestinal tract, and urinary bladder . The presence of warts on the different body parts decreases the value and aesthetic quality of the animal. There are four major types of warts such as squat, pedunculated, flat, and tags. Even though warts are a little harmful and disappear spontaneously over a long time, but appearance again of papilloma can be noticed under improper hygiene and care.